Additional Settings for Complex Nodes
Most complex processes and state diagrams make use of the Code, API Calls, Call Process, Reply to Process, Queue, and Get from Queue nodes. Basic settings are described in Node Basics and this page only covers settings unique to each node.
Code
The Code node allows you to execute JavaScript or Erlang code within a node. It consists of a Code node, a Delay node, and a Condition node working together to run the code. The Delay node is used as a circuit breaker, to limit the time that your code can run, and the Condition node catches errors in your code.
We recommend working on your code in a code editor and pasting it into the node. The Mambu Process Orchestrator (MPO) UI offers only basic validation.
 Enter your code into the window provided. You can expand the window by selecting the fullscreen icon in the corner of the code window.
Enter your code into the window provided. You can expand the window by selecting the fullscreen icon in the corner of the code window.

JavaScript
Code verification in the MPO UI will show errors for ES6 syntax or later. To turn off warnings when you use ES6 syntax such as map(), filter(), and other functions, add / * jshint esnext: true * / in the first line of your code.
To use task parameters as variables within your code, affix them after data..
Example
If we had a declared parameter called server with the value mambu, the following code prints the value mambu to the console.
console.log(data.server);
JavaScript libraries
The following libraries are included in MPO by default:
- moments.js
- moment-timezone.js
- sha1.js
- hmac-sha256.js
- md5.js
- base64.js
- aes.js
- des.js
- 3des.js
- tripledes.js
- sha512.js
Erlang
Task parameters in Erlang code are created or modified with a specifying module of any name and one main function export.
Example
The code block below adds the server parameter to a task.
-module(node).
-export([main/1]).
main(Data) -> [{<<"server">>, <<"mambu">>} | Data].
Error responses
| Return Type Tag | Return Type Description | Return Type Error | Cause |
|---|---|---|---|
| code_executing_error | error_text | software | Error in the entered code. |
| code_timeout | Timeout for executing code | hardware | The execution of the custom code timed out. The maximum execution time is 5 seconds. |
| code_return_format_error | error_text | software | The code reply is in the incorrect format. |
API Call
This node allows you to make API calls to external services using JSON, XML, or SOAP. A Delay and a Condition node are included automatically when you add an API Call node. These nodes handle errors that may arise when making calls. The Condition node determines the type of error returned and depending on the error, continues to either the Delay node to try again or ends the task with an error.
To avoid duplicating transactions in MPO - for example, when making API calls to the Mambu core - you can use idempotency keys in the API Call node.
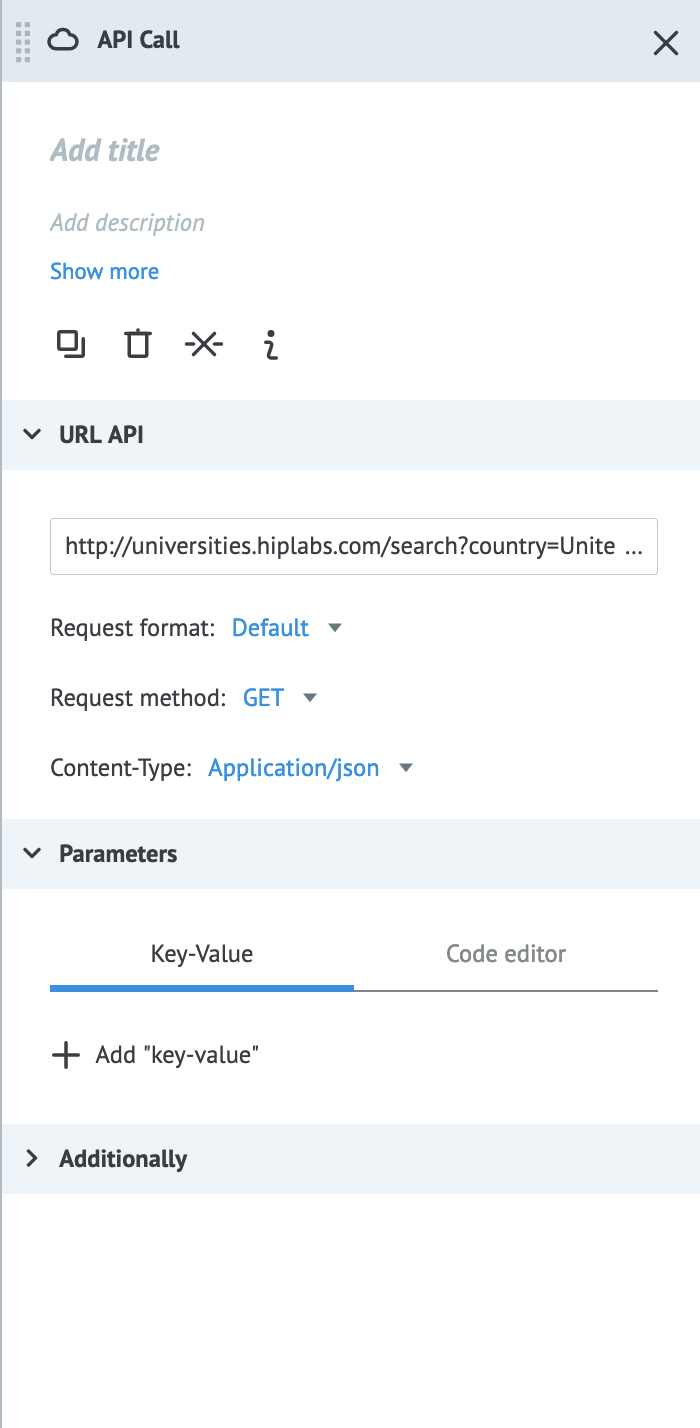
| Option | Description | Value | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| URL | The URL to retrieve data. You may use parameter values to include path parameters. | URL beginning with https:// or http:// | Yes |
| Request format | The format of the request. | Default, Corezoid, or Raw. | Yes |
| Request method | The action of the request. | GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, HEAD, or PATCH | Yes |
| Content-Type | Defines what data format is being transferred in the request. | application/json, application/x-www-form-urlencoded, application/xml, text/xml, or application/soap+xml | Yes |
Parameters
You can use parameters to declare the body of the API request or use them as path parameters in the request URL.
Additional settings
There are further options in the Additionally section, where you can:
- Set header parameters using key-value pairs.
- Customize the response parameter.
- Limit the number of simultaneous requests to the API. The default value is 5. For connectors that require high concurrency, the setting can be increased to values as high as 5,000 or 10,000. But this will affect the number of threads that MPO can spin up to handle outgoing API requests.
- Use system parameters as path parameters in the request URL by enabling Send system parameters.
- Sign the request by secret key.
- Sign the request with a certificate.
Error responses
API calls return a response code that looks like the below:
{
"__conveyor_api_return_description__": "Not valid http result json",
"__conveyor_api_return_http_code__": 405,
"__conveyor_api_return_type_error__": "software",
"__conveyor_api_return_type_tag__": "api_no_valid_json"
}
To debug an API call, find the right return HTTP code, return type error, and return type tag to diagnose the cause.
| Return Type Tag | Return Type Description | Return Type Error | Cause |
|---|---|---|---|
api_bad_answer | no_scheme | software | The API URL is empty. |
api_bad_answer | timeout or failed_connect | software | API call timed out. The maximum time to wait for an API response is 60 seconds. |
api_bad_res_data | Bad res_data: ", Data/binary, ". Please check documentation | software | The API reply contains the wrong res_data. |
api_bind_error | Error bind params to http query | hardware | Failed to add the parameters to the query. |
api_expire_query | Expire task to API, please check your api for correct answer, or increase max_threads for connections | hardware | All connections to the API have been used or the API has not answered for a long time. |
api_fatal_error | Error running api | hardware | An internal process error. |
api_no_ops | No ops. Please check documentation | software | The API response does not contain an ops block |
api_no_request_proc | Bad request_proc tag. Please fill request_proc=ok for your answer. If you want to put error use proc!=ok | software | The wrong request_proc in reply |
api_no_valid_json | Not valid http result json. | software | The request’s JSON body is invalid. |
api_task_size_overflow_limit | Your task size: {{size_data}} bytes, Max available task size: 128000 bytes, Try to change your data or try to split your task. | software | The API response is bigger than 128kb. |
api_wrong_convert_param | Param: ___, Value: ____, Try convert to: | software | Failed to convert the returned parameters. This may happen when the parameters are not XML, JSON, or images. |
The API’s HTTP response code provides the value for the "__conveyor_api_return_http_code__" key. If there are connection failures or other network issues, the HTTP code will be 0. If a successful API response contains an array, the node will return the __conveyor_api_array__ object. For more on how to use and extract data from this object, see Using the returned data.
Call Process
The Call Process node makes a synchronous call to a process to upload a task and waits for a response from that process, which will use the Reply to Process node to send back a response. To specify the process that you want to call, you must add either the Process ID or the Alias in Basic Settings > Alias or process. This will upload a new task to that process.
To send the current processes parameters to the called process, select Send all parameters. You can also declare parameters to send at this stage by selecting + Add “Key-value” or adding a JSON object in the Code editor.
Error responses
| Parameter | Description | Cause |
|---|---|---|
__conveyor_copy_task_result__ | crash_api | There was an error calling the process. |
__conveyor_copy_task_result__ | access_denied | The user does not have access rights to the called process. |
__conveyor_rpc_return_type_tag__ | rpc_task_fatal_error | There was an error calling the process. |
__conveyor_rpc_return_type_tag__ | rpc_task_size_overflow | The returned data exceeded 128kb. Try splitting your task or filtering the returned data down. |
__conveyor_rpc_return_type_tag__ | rpc_task_wrong_convert_param | The returned parameters cannot be converted to their specified type. |
Reply to Process
In order to return a response you need to add the Reply to Process node to the called process. You would add this node before every end node of the call process to ensure that a processed response is received by the calling process. In the Parameters section you define the parameters you want to return to the calling process.
The Reply to Process node from an error condition should always have the Throw exception checkbox checked. In this way, MPO knows to reply with an error to the caller process.
Queue
The Get from Queue node gets the task queue and parameters for a process. It is useful for getting data about tasks uploaded to other processes. In order to set it up, you need to add a Queue node to the process you want to get data from and a Get from Queue node to the process receiving the data. Placing the Queue node after the Start node allows you to register all the tasks uploaded to the process. The task queue is stored in the node and sends data when called by a Get from Queue node in a process.
Get from Queue
The Get from Queue node fetches data from a Queue node in another process. To set up the node you need to specify the Alias or process and the Queue node in the corresponding process in the Node input.
The returned object looks like this:
{
"__queue_task_data__": {
"{{some_key}}": "value1",
"{{some_key2}}": "value2"
},
"__queue_task_id__": "61693f97bf8a640017001203"
}
The "__queue_task_data__" object contains all the tasks parameters from the Queue node and the value of the "__queue_task_id__" key is the task ID.
Error responses
| Return Type Tag | Return Type Description | Return Type Error | Cause |
|---|---|---|---|
get_task_executing_error | not_found_task | software | The are no tasks uploaded to that process. |
get_task_executing_error | access_denied | software | The user does not have access to the process with the Queue node. |
get_task_fatal_error | Error running get task | hardware | An internal server error. |
get_task_wrong_convert_param | software | Invalid transferred process ID or node for dynamic use. Check that the process and node you picked in the Get from Queue node are correct. | |
queue_wrong_logic | No queue logic in conv_id: | software | The Queue node is missing from the process you want to get data from. |