Node Basics
Creating a process or state diagram requires nodes, which are low-code building blocks that define the logic of of a workflow. Nodes range from complex nodes, like the API Call and Condition nodes, to simpler nodes, like the Delay node.
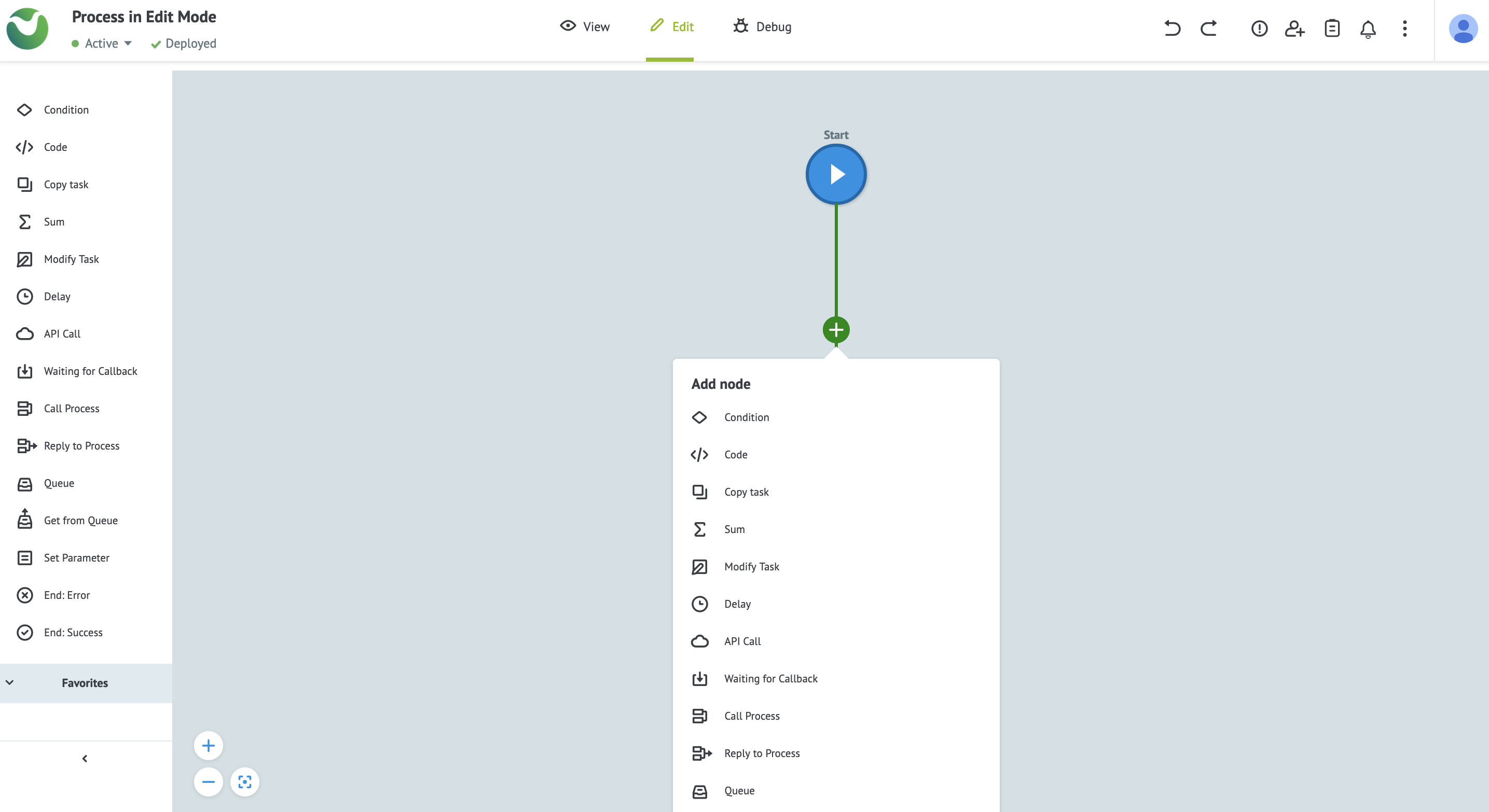
There are several ways to add a node, you may:
- select the plus (
+) sign on a connecting line and select a node to add, - select the plus sign at the bottom of an unconnected node,
- drag a new node from the node logic pane, or
- create a line between two existing nodes.
Overview
In the table, we provide a list of the available nodes. For more in-depth information about specific nodes, either select the node name or see Simple Nodes and Additional Settings for Complex Nodes.
| Name | Type | Description | Use in process? | Use in state diagram? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| API Call | Complex | Make an API call. | Yes | No |
| Call Process | Complex | Call another process. | Yes | No |
| Code | Complex | Execute JavaScript or Erlang code. | Yes | Yes |
| Condition | Simple | Evaluate logical conditions. | Yes | Yes |
| Copy Task | Simple | Copy a task from a separate process. | Yes | Yes |
| Delay | Simple | Delay the task at this point. | Yes | Yes |
| End: Error | Simple | End the task with an error. | Yes | Yes |
| End: Success | Simple | End a successfully completed task. | Yes | Yes |
| Get From Queue | Complex | Fetch task queue data. | Yes | No |
| Modify Task | Simple | Modify a task in a separate process. | Yes | Yes |
| Queue | Complex | Implement queue logic. | Yes | Yes |
| Reply to Process | Complex | Reply to a process call. | Yes | No |
| Set Parameters | Simple | Set or modify the value of a parameter. | Yes | Yes |
| Set State | Simple | This logic block allows you to define how you store a stream of data. | No | Yes |
| Sum | Simple | Sum the value of parameters. | Yes | No |
| Waiting for Callback | Simple | Wait for a reply to a request made to an external system. | Yes | No |
Common settings
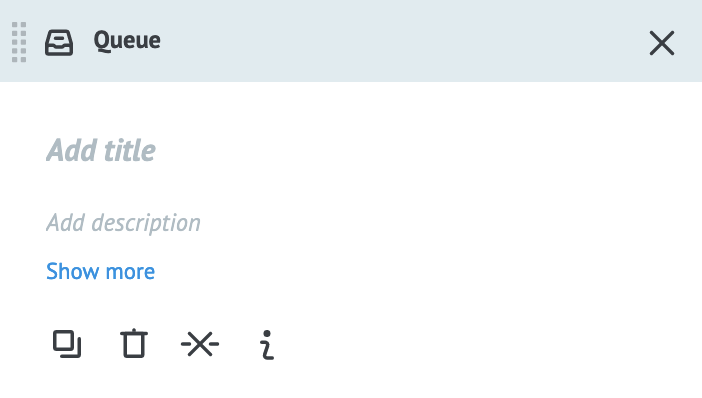
Select a node to open its settings. These may include a Basic Settings, Parameters, and an Additionally section. The settings common to all nodes are at the top and include options to Add title and Add description. Below that, the options available are Copy node, Remove node, Remove links, and Show node info.
Parameters
Parameters (or variables) can be used in most nodes. You can declare your own parameters by selecting + Add “key-value” in the Parameters section of a node, selecting the Task parameters icon in top right (next to the bell icon) to set global parameters, or by using system parameters such as these:
{{root.task_id}}: The task ID generated by the system.{{root.ref}}: The task reference.{{root.conv_id}}: The process ID.{{root.node_id}}: The node ID.{{root.prev_node_id}}: The previous node’s ID.{{root.create_time}}: The creation time of the task in unixtime.{{root.change_time}}: The modification time of task in unixtime.{{root.end_time}}: The dynamic time of timer work (for example, if you need timer to work at 8:00 AM).{{root.user_id}}: The user ID of the user who last modified the task.
Please Note:
Within Mambu Process Orchestrator (MPO), floating point numbers are rounded to six decimal places.
Additional settings
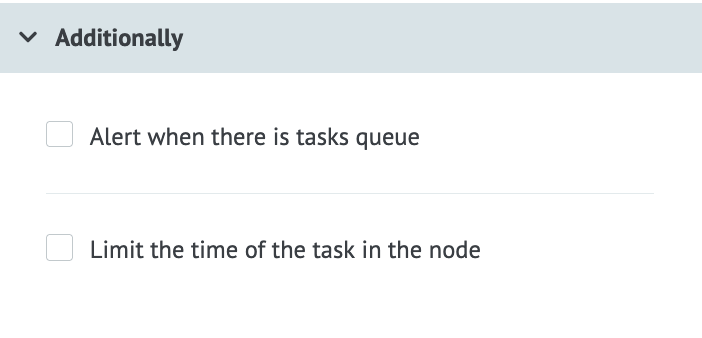
The Additionally section contains extra settings, some of which are unique to that node type. Most nodes have two common settings that you can enable: Alert when there is tasks queue, which will notify you when tasks are stuck at this node, and Limit the time of the task in the node, which limits the execution time for that particular node.
Error responses
Different types of nodes produce different error responses. To find the cause of an error, check the response table of the node. For example, for the Code node, an error in a task will produce a JSON response object with the following keys:
__conveyor_code_return_type_error__: This returns the type of error.hardware: An in-process error usually caused by a server environment failure.software: An error type usually caused by a misconfigured API Call or buggy code.
__conveyor_code_return_type_tag__: This returns an error code or short description.__conveyor_code_return_type_description__: This returns a longer description of the cause of the error and may be enough to debug the process.